GadoSpin™ P
MR angiography agent
GadoSpin™ P MRI contrast agent (1 x 5 injections): 130 - 095 - 136
GadoSpin™ P MRI contrast agent (5 x 5 injections): 130 - 095 - 137
GadoSpin P is a long-circulating imaging agent for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). It is based on a high molecular weight polymer that does not extravasate from intact blood vessels.
The unique polymeric gadolinium chelate agent:
- Is based on a linear polymer of a tailored molecular weight
- Has a long blood half-life, remaining in the vasculature for a prolonged period of time
- Enables higher resolution images through a longer steady state period and a wide acquisition timeframe
- GadoSpin P is Viscover's leading blood pool agent for MR angiography
- Effectively visualize healthy vasculature
- Visualize and quantify vascular abnormalities in tumors and inflammation
- Harness the full potential of your imaging device to investigate microvessels
Apply GadoSpin P to:
Relaxivity (37 °C, 1.41T)
r1 = 10 L mmol-1 s-1
r2 = 12 L mmol-1 s-1
~200,000 g mol-1
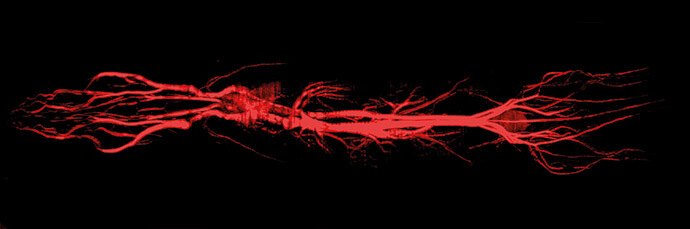
Schematic diagram of GadoSpin P:
- Ahn, J.H. et al. (2019) Meningeal lymphatic vessels at the skull base drain cerebrospinal fluid. Nature 572(7767): 62-66.
- Govaerts, K. et al. (2013) Towards quantitative evaluation of vascular alterations in mice using MR angiography.
Front. Neuroinform. doi: 10.3389/conf.fninf.2013.10.00021. - Yang, L.et al. (2013) Evaluating glymphatic pathway function utilizing clinically relevant intrathecal infusion of CSF tracer. J. Transl. Med. 11: 107.
- Iliff, J.J. et al. (2013) Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J Clin Invest. 123(3): 1299-309.

