GadoSpin™ V
Liver imaging MRI agent
GadoSpin™ V MRI contrast agent (1 x 5 injections): 130 - 095 - 705
GadoSpin™ V MRI contrast agent (5 x 5 injections): 130 - 095 - 706
GadoSpin V is an extracellular MRI agent specifically developed for liver imaging. It is based on the proven gadoxetate disodium molecule that has long been used in clinical practice. The agent provides positive contrast by accumulating in healthy liver tissue and enables detection of focal liver lesions in T1-weighted MRI.
The proven liver imaging MRI agent from clinical practice:
- Serves as a reference imaging agent
- Accumulates in hepatocytes through active transport
- Enables detection and characterization of focal liver lesions
- Is optimized for the visualization even of tiny liver lesions
Rely on a substance that is well-proven in clinical practice to:
- Positively enhance healthy liver tissue in T1-weighted MR images
- Effectively visualize liver tumors and metastases
- Differentiate malignant and benign lesions
Relaxivity (37 °C, 1.5 T)
r1 = 7 L mmol-1 s-1
r2 = 9 L mmol-1 s-1
r1 = 7 L mmol-1 s-1
726 g mol-1
Structural formula of Gd-EOB-DTPA Disodium
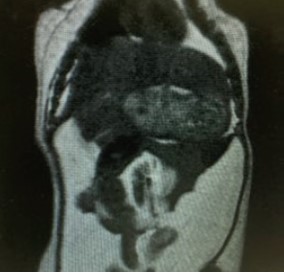
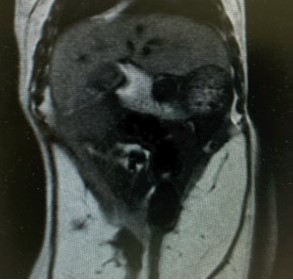
- Kiryu, S. et al. (2009) Evaluation of gadoxetate disodium as a contrast agent for mouse liver imaging: comparison with gadobenate dimeglumine. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 27(1): 101-107.
- Freimuth, J. et al. (2010) Freimuth, J. et al. (2010) Application of magnetic resonance imaging in transgenic and chemical mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Molecular Cancer 9: 94.
- Yang, L. et al. (2020) T1 Mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for the prediction of oxaliplatin-induced liver injury in a mouse model. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 53: 896–902.

